सब्ज़ी

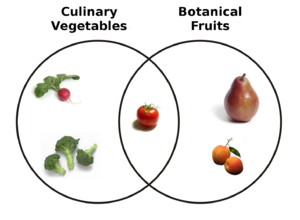
सब्जी किसी पौधे के उस भाग को कहते हैं जिसे आँच पर पकाकर खाया जाता है। बीजों और मीठे फलों को प्रायः सब्जी नहीं कहा जाता है। खाए जाने वाले पत्ते, तने, डंठल और जड़ें प्रायः सब्जी कही जाती हैं। सांस्कृतिक दृष्टि से 'सब्जी' की परिभाषा स्थानीय प्रथा के अनुसार अलग-अलग होती है। उदाहरण के लिए बहुत से लोग कुकुरमुत्तों (मशरूमों) को सब्ज़ी मानते हैं (हालाँकि जीववैज्ञानिक दृष्टि से यह 'पौधे' नहीं समझे जाते) जबकि अन्य लोगों के अनुसार यह सब्ज़ी नहीं बल्कि एक अन्य खाने की श्रेणी है।[1][2]
कुछ सब्ज़ियाँ कच्ची खाई जा सकती हैं जबकि अन्य सब्ज़ियों को पकाना पड़ता है। आम-तौर पर सब्ज़ियों को नमक या खट्टाई के साथ पकाया जाता है लेकिन कुछ सब्ज़ियाँ ऐसी भी हैं जिन्हें चीनी के साथ पकाकर उनकी मिठाई या हलवे बनाए जाते हैं (जैसे गाजर)।
शब्द की जड़ें
'सब्ज़' शब्द का मतलब आधुनिक फ़ारसी में 'हरा', या कभी-कभी 'काला' होता है। फ़ारसी में 'सब्ज़ी' केवल वास्तव में हरे रंग के पत्तों-सब्ज़ियों को बुलाया जाता है जबकि हिन्दी, उर्दू, पंजाबी, कश्मीरी और उत्तरी भारतीय उपमहाद्वीप की अन्य भाषाओँ में 'सब्ज़ी' की श्रेणी में किसी भी रंग की सब्ज़ियाँ शामिल हैं। ध्यान दें कि संस्कृत और फ़ारसी हिन्द-ईरानी भाषा परिवार की बहनें होने के कारण हज़ारों सजातीय शब्द रखती हैं और 'सब्ज़' भी इनमें से एक है। संस्कृत में इसी शब्द का रूप 'सस्य' है, जिसका मूल अर्थ '(खाया जाने वाला) दाना या फल' था।[3]
प्रमुख सब्जियाँ
| Some common vegetables | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| चित्र | प्रजाति | कौन सा भाग | उत्पत्ति | Cultivars | World production (×106 tons, 2012)[4] |
 | पत्ता गोभी | leaves, axillary buds, stems, flower heads | Europe | cabbage, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, broccoli, kale, kohlrabi, red cabbage, Savoy cabbage, Chinese broccoli, collard greens | 70.1 |
 | Brassica rapa | root, leaves | Asia | turnip, Chinese cabbage, napa cabbage, bok choy | |
 | Raphanus sativus | root, leaves, seed pods, seed oil, sprouting | Southeastern Asia | radish, daikon, seedpod varieties | |
 | गाजर | root, leaves, stems | Persia | गाजर | 36.9[n 1] |
 | Pastinaca sativa | root | Eurasia | parsnip | |
 | Beta vulgaris | root, leaves | Europe and Near East | beetroot, sea beet, Swiss chard, sugar beet | |
 | Lactuca sativa | leaves, stems, seed oil | Egypt | lettuce, celtuce | 24.9 |
 | Phaseolus vulgaris Phaseolus coccineus Phaseolus lunatus | pods, seeds | Central and South America | green bean, French bean, runner bean, haricot bean, Lima bean | 44.6[n 2] |
 | Vicia faba | pods, seeds | Mediterranean and Middle East | broad bean | |
 | Pisum sativum | pods, seeds, sprouts | Mediterranean and Middle East | pea, snap pea, snow pea, split pea | 28.9[n 2] |
 | Solanum tuberosum | tubers | South America | potato | 365.4 |
 | Solanum melongena | fruits | South and East Asia | eggplant (aubergine) | 48.4 |
 | Solanum lycopersicum | fruits | South America | tomato, see list of tomato cultivars | 161.8 |
 | Cucumis sativus | fruits | Southern Asia | cucumber, see list of cucumber varieties | 65.1 |
 | Cucurbita spp. | fruits, flowers | Mesoamerica | pumpkin, squash, marrow, zucchini (courgette), gourd | 24.6 |
 | Allium cepa | bulbs, leaves | Asia | onion, spring onion, scallion, shallot, see list of onion cultivars | 87.2[n 2] |
 | Allium sativum | bulbs | Asia | garlic | 24.8 |
 | Allium ampeloprasum | leaf sheaths | Europe and Middle East | leek, elephant garlic | 21.7 |
 | Capsicum annuum | fruits | North and South America | pepper, bell pepper, sweet pepper | 34.5[n 2] |
 | Spinacia oleracea | leaves | Central and southwestern Asia | spinach | 21.7 |
 | Dioscorea spp. | tubers | Tropical Africa | yam | 59.5 |
 | Ipomoea batatas | tubers, leaves, shoots | Central and South America | sweet potato, see list of sweet potato cultivars | 108.0 |
 | Manihot esculenta | tubers | South America | cassava | 269.1 |
प्रमुख उत्पादक देश
सन २०१० में विश्व में सब्जियों का सबसे बड़ा उत्पादक चीन था और उसके बाद भारत।[5]
| देश | खेती का क्षेत्रफल हजार हेटेयर (2,500 एकड़) | उत्पादन हजार किलो /हेक्टेअयर | उत्पादन हजार टन |
|---|---|---|---|
| चीन | 23,458 | 230 | 539,993 |
| भारत | 7,256 | 138 | 100,045 |
| संयुक्त राज्य | 1,120 | 318 | 35,609 |
| तुर्की | 1,090 | 238 | 25,901 |
| ईरान | 767 | 261 | 19,995 |
| मिस्र | 755 | 251 | 19,487 |
| इटली | 537 | 265 | 14,201 |
| Russia | 759 | 175 | 13,283 |
| Spain | 348 | 364 | 12,679 |
| Mexico | 681 | 184 | 12,515 |
| Nigeria | 1844 | 64 | 11,830 |
| Brazil | 500 | 225 | 11,233 |
| Japan | 407 | 264 | 10,746 |
| Indonesia | 1082 | 90 | 9,780 |
| South Korea | 268 | 364 | 9,757 |
| Vietnam | 818 | 110 | 8,976 |
| Ukraine | 551 | 162 | 8,911 |
| Uzbekistan | 220 | 342 | 7,529 |
| Philippines | 718 | 88 | 6,299 |
| France | 245 | 227 | 5,572 |
| Total world | 55,598 | 188 | 1,044,380 |
सन्दर्भ
- ↑ Suggestions - Vegetables Archived 2012-03-01 at the वेबैक मशीन, Cooks.com, Accessed on 2009-06-24.
- ↑ Alternative Crops and Plants: Vegetables and Mushrooms Archived 2012-02-17 at the वेबैक मशीन. United States Department of Agriculture. Last modified on 2009-06-08. Retrieved 2009-06-24.
- ↑ Priyadarshi, P. 2010. Recent Studies in Indian Archaeo-linguistics and Archaeo-genetics having bearing on Indian Prehistory, Joint Annual Conference of Indian Archaeology Society, Indian Society for Prehistoric and Quaternary Studies, Indian History and Culture Society, Lucknow, 30 दिसम्बर 2010. ... We can now have a look at some of the farming related words in the Indo-European languages ... *sehm (PIE, grain), sasa (Sanskrit; sasam in Rig-Veda), sasya (Sanskrit, food, seed, grain, herb), sas (Kashmiri, beans, peas, lentils), sas (Bangla, grain, fruit), sasa (Oriya, kernel, nutritious part), sabz (Iranian, green vegetable), sem (Hindi, beans) ...
- ↑ "FAOSTAT Query page". मूल से 2015-09-06 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 2015-09-16. Aggregate data: may include official, semi-official or estimated data
- ↑ "Table 27 Top vegetable producers and their productivity" (PDF). FAO Statistical Yearbook 2013. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. पृ॰ 165. मूल से 15 जुलाई 2017 को पुरालेखित (PDF). अभिगमन तिथि 2015-09-14.
इन्हें भी देखें
बाहरी कड़ियाँ

