उर्जा रूपान्तरण की दक्षता
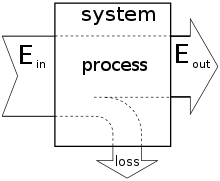
उर्जा का रूपान्तरण करने वाली किसी मशीन या तन्त्र के निर्गम (आउटपुट) और निवेश (इनपुट) उर्जाओं के अनुपात (रेशियो) को उस मशीन की उर्जा रूपान्तरण की दक्षता (Energy conversion efficiency) कहते हैं।
उर्जा रूपान्तरण की दक्षता के कुछ प्रमुख उदाहरण
| ऊर्जा-रूपान्तरण का प्रक्रम | ऊर्जा-रूपान्तरण का प्रकार | ऊर्जा दक्षता |
|---|---|---|
| विद्युत उत्पादन | ||
| गैस टर्बाइन | ऊष्मा से विद्युत ऊर्जा | 40% तक |
| गैस टर्बाइन के साथ भाप टरबाइन (संयुक्त चक्र) | ऊष्मा से विद्युत ऊर्जा | 60% तक |
| जल टर्बाइन | गुरुत्वीय से विद्युत | 90% तक (व्यावहारिक रूप में प्राप्त किया गया) |
| पवन टर्बाइन | Kinetic to electrical | up to 59% (theoretical limit) |
| सौर सेल | Radiative to electrical | 6–40% (technology-dependent, 15-20% most often, 85–90% theoretical limit) |
| ईंधन सेल | रासायनिक ऊर्जा से विद्युत ऊर्जा | up to 85% |
| विश्व का कुल विद्युत उत्पादन (2008 में) | Gross output 39% | Net output 33%[1] |
| Electricity storage | ||
| लिथियम-ऑयन बैटरी | Chemical to electrical/reversible | 80–90% [2] |
| Nickel-metal hydride battery | Chemical to electrical/reversible | 66% [3] |
| Lead-acid battery | Chemical to electrical/reversible | 50–95% [4] |
| Engine/motor | ||
| Combustion engine | Chemical to kinetic | 10–50%[5] |
| Electric motor | Electrical to kinetic | 70–99.99% (> 200 W); 50–90% (10–200 W); 30–60% (< 10 W) |
| Turbofan | Chemical to kinetic | 20-40%[6] |
| Natural process | ||
| Photosynthesis | Radiative to chemical | 0.1% (average)[7] to 2% (best);[8] up to 6% in principle[9] (see main: Photosynthetic efficiency) |
| Muscle | Chemical to kinetic | 14–27% |
| Appliance | ||
| Household refrigerator | Electrical to thermal | low-end systems ~ 20%; high-end systems ~ 40–50% |
| Incandescent light bulb | Electrical to radiative | 0.7–5.1%,[10] 5–10%[] |
| Light-emitting diode (LED) | Electrical to radiative | 4.2–53% [11] |
| Fluorescent lamp | Electrical to radiative | 8.0–15.6%,[10] 28%[12] |
| Low-pressure sodium lamp | Electrical to radiative | 15.0–29.0%,[10] 40.5%[12] |
| Metal-halide lamp | Electrical to radiative | 9.5–17.0%,[10] 24%[12] |
| Switched-mode power supply | Electrical to electrical | currently up to 96% practically |
| Electric shower | Electrical to thermal | 90–95% (multiply by the energy efficiency of electricity generation to compare with other water-heating systems) |
| Electric heater | Electrical to thermal | ~100% (essentially all energy is converted into heat, multiply by the energy efficiency of electricity generation to compare with other heating systems) |
| Others | ||
| Firearm | Chemical to kinetic | ~30% (.300 Hawk ammunition) |
| Electrolysis of water | Electrical to chemical | 50–70% (80–94% theoretical maximum) |
सन्दर्भ
- ↑ IEC/OECD 2008 Energy Balance for World Archived 2013-07-24 at the वेबैक मशीन, accessdate 2011-06-08
- ↑ Valøen, Lars Ole and Shoesmith, Mark I. (2007). The effect of PHEV and HEV duty cycles on battery and battery pack performance (PDF). 2007 Plug-in Highway Electric Vehicle Conference: Proceedings. Retrieved 11 June 2010.
- ↑ "NiMH Battery Charging Basics". PowerStream.com.
- ↑ PowerSonic, Technical Manual (PDF), p. 19, retrieved January 2014
- ↑ "Motivations for Promoting Clean Diesels" (PDF). US Department Of Energy. 2006. मूल (PDF) से October 7, 2008 को पुरालेखित.
- ↑ "11.5 Trends in thermal and propulsive efficiency". web.mit.edu. मूल से 28 मई 2013 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 2016-10-26.
- ↑ Govindjee, What is photosynthesis? Archived 2009-05-06 at the वेबैक मशीन
- ↑ The Green Solar Collector; converting sunlight into algal biomass Archived 2009-10-05 at the वेबैक मशीन Wageningen University project (2005—2008)
- ↑ Miyamoto K. "Chapter 1 - Biological energy production". Renewable biological systems for alternative sustainable energy production (FAO Agricultural Services Bulletin - 128). Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. मूल से 7 सितंबर 2013 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 2009-01-04.
- ↑ अ आ इ ई Luminous efficacy#Lighting efficiency
- ↑ "All in 1 LED Lighting Solutions Guide". PhilipsLumileds.com. Philips. 2012-10-04. पृ॰ 15. मूल (PDF) से 2013-03-31 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 2015-11-18.
- ↑ अ आ इ Light Pollution Handbook. Springer. 2004. मूल से 27 जून 2014 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 31 दिसंबर 2019.
