आर (प्रोग्रामन भाषा)
| R logo.svg | |
| पहला अवतरण | अगस्त 1993[1] |
|---|---|
| डिज़ाइनर | Ross Ihaka and Robert Gentleman |
| निर्माता | R Core Team[2] |
| स्थायी विमोचन | 3.5.2 ("Eggshell Igloo")[3] (दिसम्बर 20, 2018) |
| लिखने का तरिका | Dynamic |
| प्रभावकर्ता | |
| प्रभावित | Julia[4] |
| अनुज्ञप्तिधारी | GNU GPL v2[5] |
| सामान्य संचिका नाम अनुयोजन | .r, .R, .RData, .rds, .rda |
| वेबसाइट | www |
आर (R) कम्प्यूटर की एक प्रोग्रामन भाषा है जो विशेषत: सांख्यिकी से संबन्धित गणना करने एवं ग्राफ आदि बनाने हेतु उपयोगी है। यह भाषा विश्व के सांख्यिकीविदों में सांख्यिकी से सम्बन्धित सॉफ्ट्वेयरों के निर्माण के लिये मानक भाषा जैसे प्रचलित हो गयी है।
उदाहरण
मूलभूत सिन्टैक्स
निम्नलिखित उदाहरण भाषा के मूल वाक्यविन्यास और कमांड-लाइन इंटरफ़ेस के उपयोग को दर्शाते हैं।
In R, the generally preferred[6] assignment operator is an arrow made from two characters <-, although = can usually be used instead.[7]
> x <- 1:6 # Create vector.
> y <- x^2 # Create vector by formula.
> print(y) # Print the vector’s contents.
[1] 1 4 9 16 25 36
> mean(y) # Arithmetic mean of vector.
[1] 15.16667
> var(y) # Sample variance of vector.
[1] 178.9667
> model <- lm(y ~ x) # Linear regression model y = A + B * x.
> print(model) # Print the model’s results.
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x)
Coefficients:
(Intercept) x
-9.333 7.000
> summary(model) # Display an in-depth summary of the model.
Call:
lm(formula = y ~ x)
Residuals:
1 2 3 4 5 6
3.3333 -0.6667 -2.6667 -2.6667 -0.6667 3.3333
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) -9.3333 2.8441 -3.282 0.030453 *
x 7.0000 0.7303 9.585 0.000662 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 3.055 on 4 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.9583, Adjusted R-squared: 0.9478
F-statistic: 91.88 on 1 and 4 DF, p-value: 0.000662
> par(mfrow = c(2, 2)) # Create a 2 by 2 layout for figures.
> plot(model) # Output diagnostic plots of the model.

फ्ंक्शन की संरचना
One of R’s strengths is the ease of creating new functions. Objects in the function body remain local to the function, and any data type may be returned.[8] Here is an example user-created function:
# Declare function “f” with parameters “x”, “y“
# that returns a linear combination of x and y.
f <- function(x, y) {
z <- 3 * x + 4 * y
return(z)
}
> f(1, 2)
[1] 11
> f(c(1,2,3), c(5,3,4))
[1] 23 18 25
> f(1:3, 4)
[1] 19 22 25
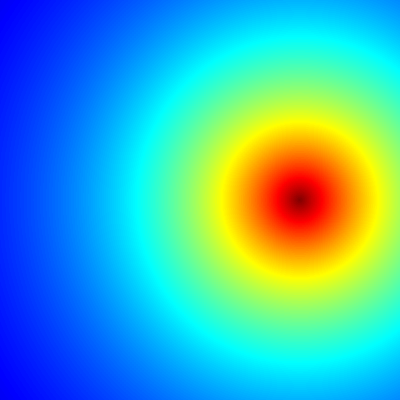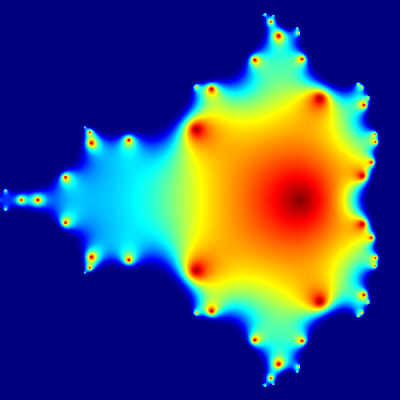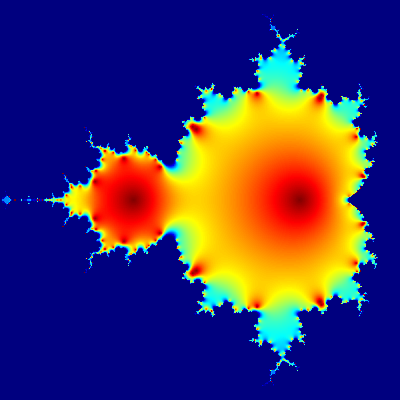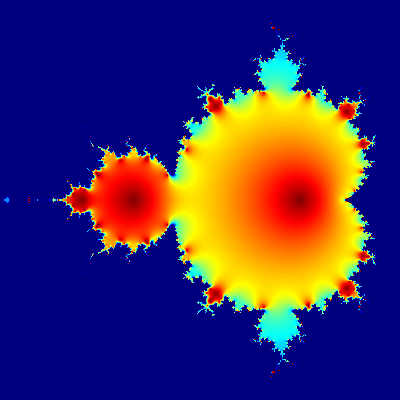
Mandelbrot set
Short R code calculating Mandelbrot set through the first 20 iterations of equation z = z2 + c plotted for different complex constants c. This example demonstrates:
- use of community-developed external libraries (called packages), in this case caTools package
- handling of complex numbers
- multidimensional arrays of numbers used as basic data type, see variables
C,ZandX.
install.packages("caTools") # install external package
library(caTools) # external package providing write.gif function
jet.colors <- colorRampPalette(c("red", "blue", "#007FFF", "cyan", "#7FFF7F",
"yellow", "#FF7F00", "red", "#7F0000"))
dx <- 1500 # define width
dy <- 1400 # define height
C <- complex(real = rep(seq(-2.2, 1.0, length.out = dx), each = dy),
imag = rep(seq(-1.2, 1.2, length.out = dy), dx))
C <- matrix(C, dy, dx) # reshape as square matrix of complex numbers
Z <- 0 # initialize Z to zero
X <- array(0, c(dy, dx, 20)) # initialize output 3D array
for (k in 1:20) { # loop with 20 iterations
Z <- Z^2 + C # the central difference equation
X[, , k] <- exp(-abs(Z)) # capture results
}
write.gif(X, "Mandelbrot.gif", col = jet.colors, delay = 100)
बाहरी कड़ियाँ
- The R wiki is a community wiki for R.
- R books has an extensive list (with brief comments) of books related to R.
- The R Graphical Manual[मृत कड़ियाँ] provides a collection of R graphics from all R packages, as well as an index to all functions in all R packages.
- The R Wikibook.
सन्दर्भ
- ↑ अ आ साँचा:Cite techreport
- ↑ Hornik, Kurt (November 26, 2015). "R FAQ". The Comprehensive R Archive Network. 2.1 What is R?. मूल से 9 जुलाई 2011 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 2018-08-05.
- ↑ "The Comprehensive R Archive Network". मूल से 23 जनवरी 2019 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 2018-12-26.
- ↑ "Introduction". The Julia Manual. मूल से 20 जून 2018 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 5 अगस्त 2018.
- ↑ "R license". r-project. मूल से 13 जनवरी 2019 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 2018-08-05.
- ↑ most used assignment operator in R is
<-- R Development Core Team. "Writing R Extensions". मूल से 6 जनवरी 2019 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 2018-09-11.
[...] we recommend the consistent use of the preferred assignment operator ‘<-’ (rather than ‘=’) for assignment.
- "Google's R Style Guide". मूल से 11 जनवरी 2019 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 2018-09-11.
- Wickham, Hadley. "Style Guide". मूल से 7 जनवरी 2019 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 2018-09-11.
- Bengtsson, Henrik (January 2009). "R Coding Conventions (RCC) – a draft". मूल से 19 मार्च 2016 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 2018-09-11.
- R Development Core Team. "Writing R Extensions". मूल से 6 जनवरी 2019 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 2018-09-11.
- ↑ R Development Core Team. "Assignments with the = Operator". मूल से 8 जनवरी 2019 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 2018-09-11.
- ↑ Kabacoff, Robert (2012). "Quick-R: User-Defined Functions". statmethods.net. मूल से 7 जनवरी 2019 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 2018-09-28.